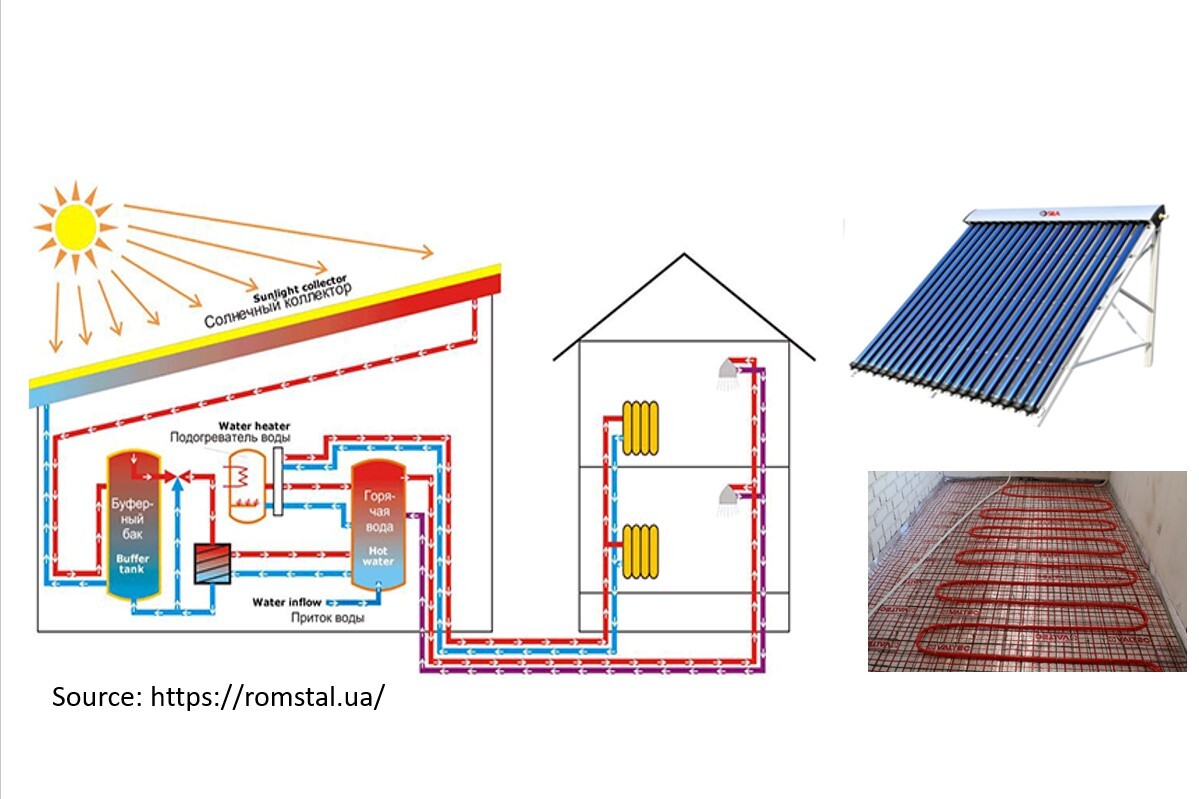
A solar collector is a solar installation (for collecting the thermal energy of the sun), capable of heating the heat-transfer material. Unlike solar panels that produce electricity directly, the solar collector heats the heat-transfer material. The solar collector is used to heat the water in the water tank, which is used for washing purposes. Solar collectors are flat and vacuum.
The principle of operation of solar collectors. The design of the vacuum collector is as follows: there are several vacuum glass tubes, inside which there is an absorbing plate connected to a heat pipe. The heat pipe heats up, and from its end the heat is transferred to the coolant, which is the propylene glycol mixture. A vacuum is created around the tube, which significantly reduces heat loss. This makes vacuum collectors more efficient than flat-plate collectors, especially in cold conditions. A gap is formed between the collector pipes, through which snow falls, which reduces the percentage of losses in the production of heat in snowy conditions. However, the pipes do not produce heat radiation, so the fallen snow will not melt.
Today on the market there are many installations from 100 liters and above, which are suitable not only for the hot water supply of a shower room, but also for heating a building. To reheat the coolant, it is planned to install electric heating elements in storage tanks.
In order for the heating system with solar collectors to work more efficiently, it is recommended to combine it with a water heated floor system. The principle of operation is simple: electric wires (mats), IR film or pipes for a water floor are placed under the finishing floor covering, which act as heating devices. The efficiency of such a system is due to the fact that it is enough to heat the coolant to 30 - 40 ° C, and not to 70 ° C, as in a radiator system.